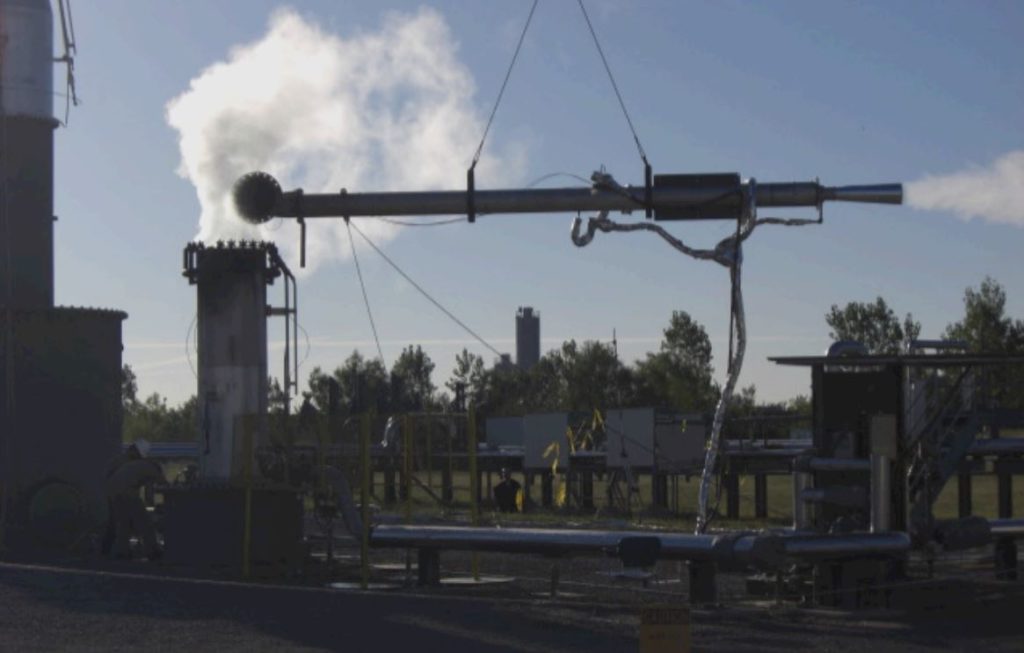

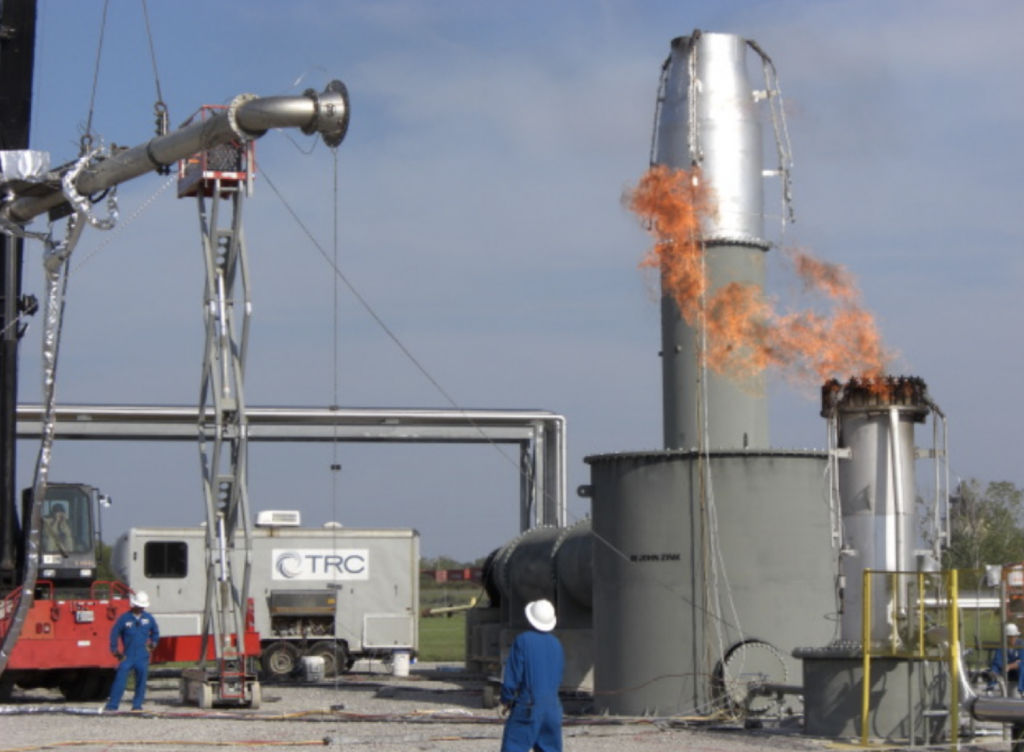
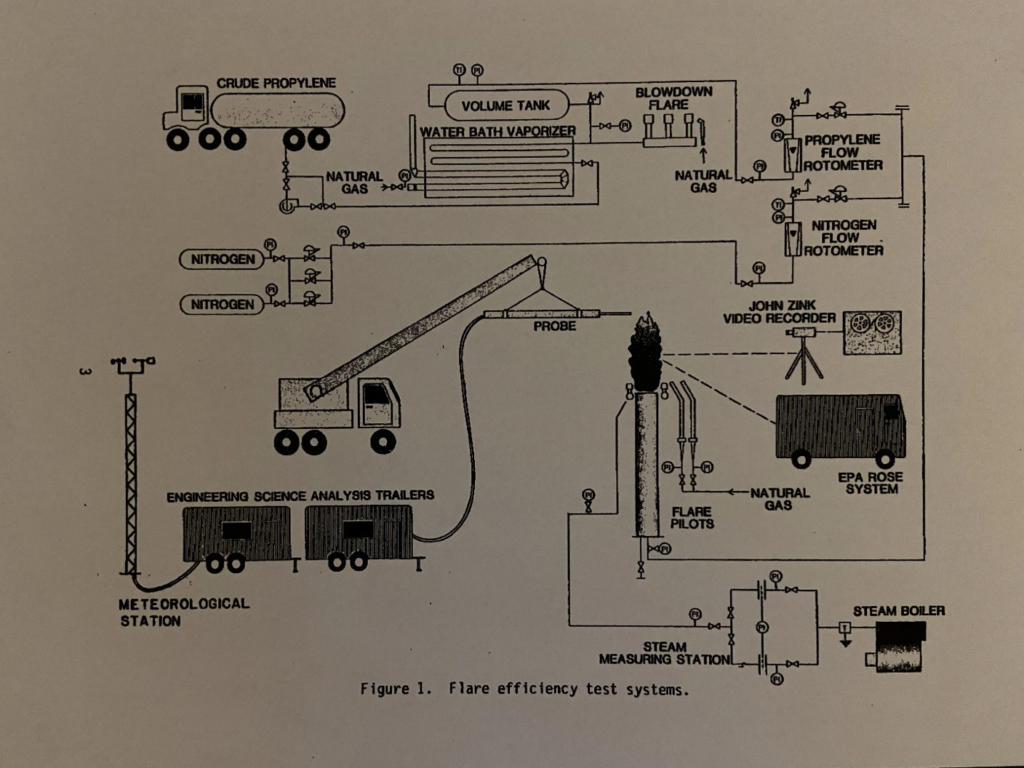
Extractive samplingThe process of measuring flaring combustion by extracting part of the plume and analysing the absolute quantities of burnt and unburnt gas by measn of a traceable method such as… Learn more… has for several decades been considered the nearest technique to a reference method for measuring flare combustion efficiency and destruction efficiency. The method involves taking gas samples in the vicinity of a test flare by means of an extractive hood suspended over the flare. Gas samples are analysed for hydrocarbons and combustion products by means of gas chromatography (GC-MS).
The key advantage is the ability to directly measure the composition of gas relative to traceableWherby a measurement is calibrated to a reference standard and when the uncertainties of th calibration are insignificant compared to the uncertainties arising from random effects or from a limited number… Learn more… reference gases. However, the limitations are that it is resource intensive, requires experienced operators and specially built test facilities. It cannot be deployed in the field to measure combustion from existing flares. Test facilities do not cover the full range of flare sizes in use today.

Advantages
Chromatography analysers are mature technology with the capability to provide accurate continuous measurements traceable to calibration gases with a known level of uncertainty
Experimental facilities have been configured to cover a wide range of flare types and gas mixtures including those using assist gases
It allows a direct calculation of combustion and destruction efficiencies based on measured gas compositions rather than using secondary parameters
Sampling probe can be designed to operate during a wide range of weather conditions
Extractive sampling enables the operator to measure the composition of any gas of interest
Limitations
It is a highly resource intensive method requiring personnel to operate the system and the presence of mobile or permanent laboratory facilities nearby for sampling and analysis
Positioning of the extraction hood is critical to the success of the method
Whilst considered the nearest thing to a reference method, the technique is not taking all of the gases from the combustion zone and so the area that is being sampled has to be considered representative of the total flare
The position of the sampling may need to be adjusted once the wind conditions change to take representative samples
Cannot be field deployed – and therefore cannot measure flares under operational conditions (such as over water) or over extended time periods
Very few facilities exist in the world that can offer this measurement as a service
Case study
Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) has conducted a thorough study in 2010 (TCEQ 2010 Flare Study) of various flare destruction efficiency measurement techniques using extractive sampling as a reference method. It was also used to investigate optimal operating parameters for air and steam assisted flares.
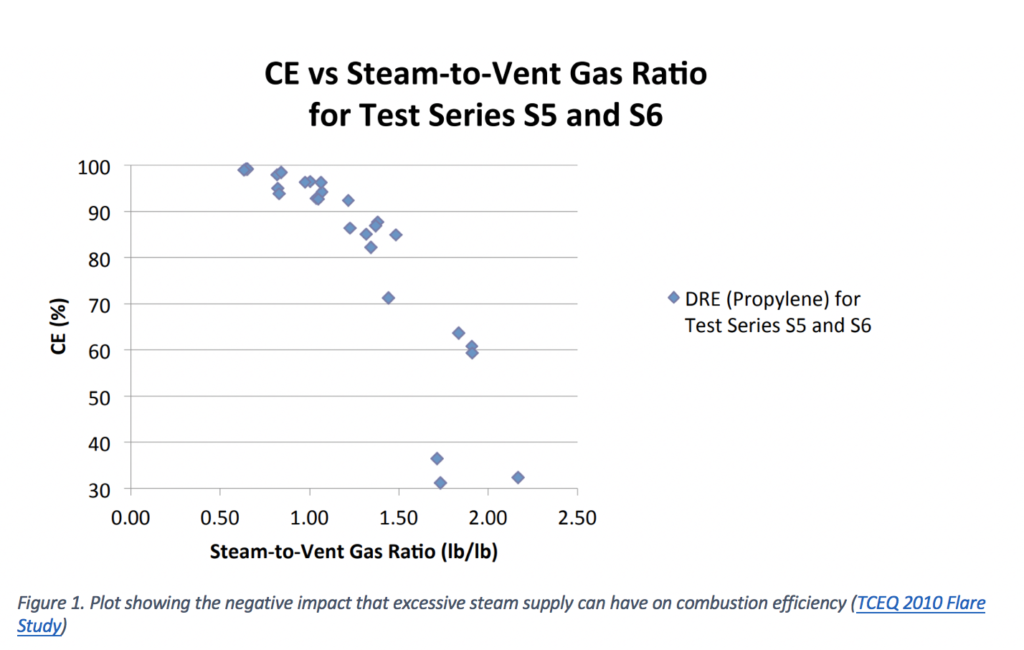
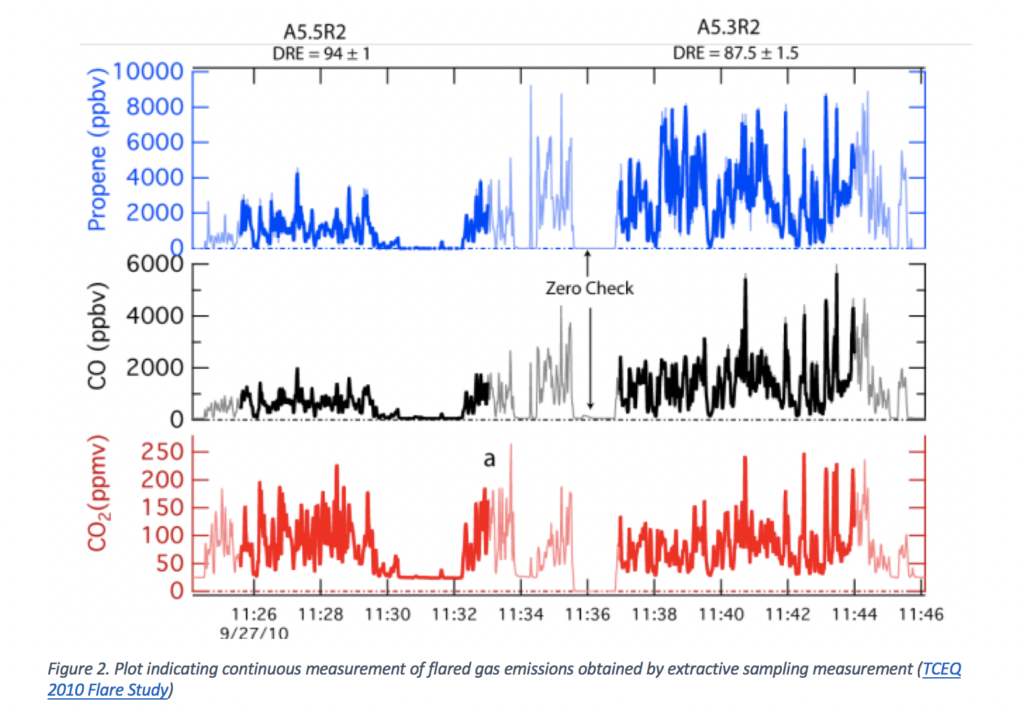
Figure 1 shows that while steam is used to increase the flare performance, excessive steam supply to the flare tip can dramatically reduce the flare destruction efficiency. Figure 2 indicates the results obtained using extractive sampling method, which allows to directly measure different gas species compositions.
The challenges in measuring flare efficinecy in the field have led to a number of empirical studies being designed using both full scale and reduced sacale flares with additional instrumentation designed to analyse the flare products. Whilst these provide useful insights in to flare performance cautuion is required to consider how close the experimental design replicates in-field conditions including environmental effects.