
Summary
Process simulation is used for the design, development, analysis, and optimisation of technical processes such as: chemical plants, chemical processes, power stations, oil and gas facilities, biological processes, and similar technical functions.
In the event, that the flowrate and composition of fluids in a flare system cannot be directly measured, and their subsequent emissions calculated, process simulation could be deployed to assist in determining certain data.
How it Works
Process simulation is a model-based representation of chemical, physical, biological, or other technical processes and unit operations in software.
Process simulations can estimate the composition of streams flowing within a process facility under both normal operating conditions and also during abnormal, upset conditions.
If some streams are directed to the flare or atmospheric vent under certain circumstances, then these situations can be modelled and the flowrate and composition of these flared and vented streams can be predicted.
These simulations can provide valuable information on potential emissions if other flare measurement and analysis equipment is not installed on a facility.
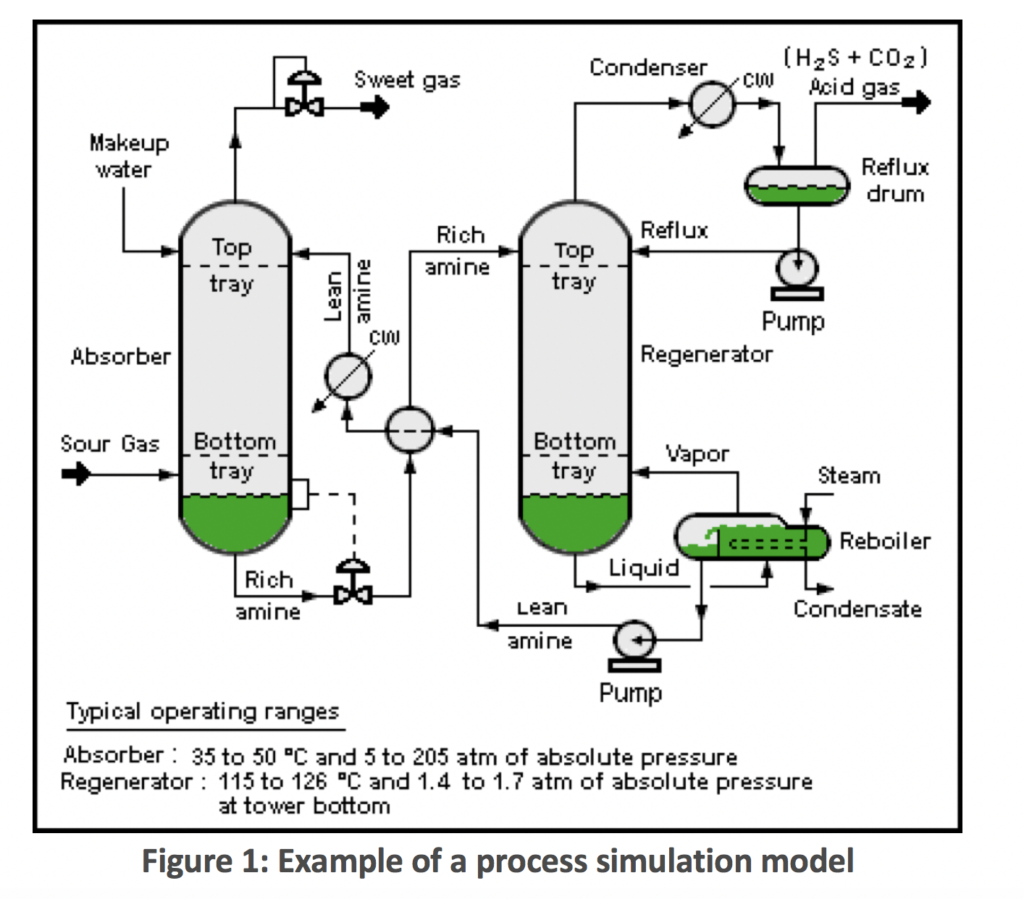
Implementing Process Simulation for flare systems is not widely used in the Oil and Gas Industry.
Advantages
No installed equipment required
Equipment costs.
Limitations
High level of expertise required to build and use simulation models
Periodic updates
Low accuracy
High uncertainty
Case study
No case study available at this time.
Engineering calculations are performed by using design parameters to calculate flow in the flare line in the absence of installed instrumentation or in addition to installed instrumentation