
A pitot tube or probe, is a device used to measure the velocity of a flowing fluid.
How it Works
The basic pitot tube consists of a tube inserted into a pipe and pointing directly into the fluid flow. In the tube the moving fluid is brought to rest (stagnates) as there is no outlet to allow flow to continue, and its stagnation pressure can be measured.
The pressure of the fluid flowing around the outside of the pitot tube can also be measured and is known as the static pressure.
The difference between the stagnation pressure and the static pressure can be used to determine the velocity of the fluid flowing inside the main pipe.
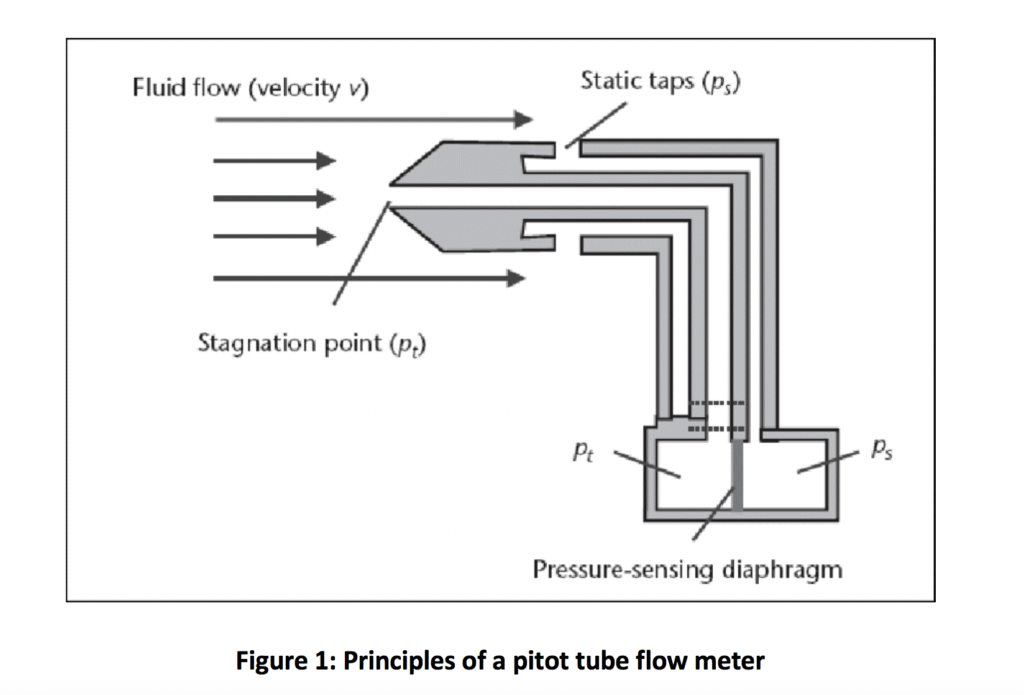
(Image taken from researchgate.net)
Advantages
Well proven, simple, and robust metering principle
Low cost
Limitations
Not suited for low flow velocities since the difference in measured pressures is very low
High risk of contamination of flow element (pitot tube)
Pitot tube projects out into flare line
Entrained liquids can be problematic for pitot tubes
Limited turndown ratio, typically 4:1
Can be damaged by wake induced vibration at high gas velocities
Go Deeper
Case study
No case study available at this time.
Differential pressure meters work on the principle of calculating a flow rate based on the change in pressure between two measured points.