
Predictive analytics describes the process by which measured parameters and models are combined to derive information on flare efficiency. They are analogous to Predictive Emissions Monitoring (PEMS) systems used to track emissions of pollutants such as NOx from gas turbines. For flares, predictive analytics system uses a method based on a parametric modelA Parametric Model is a concept used in statistics to describe a model in which all its information is represented within its parameters. In short, the only information needed to… Learn more… and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFDis a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and data structures to analyse and solve problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate… Learn more…) studies with input data coming from flare gas composition, flow rates, flare design and environmental factors such as wind speed. Predictive systems has the advantage of being permanently installed, providing continuous and near real-time feedback on flare performance, allowing adaptations to be made to maintain efficient combustion. Currently available systems are independent of flare vendor and control system provider.
Analytics work as a reporting and monitoring tool, but have also been successfully deployed with feedback loops for the management of flares by moderating steam and air assist gases. Their use for methane management remains an area of technology development.
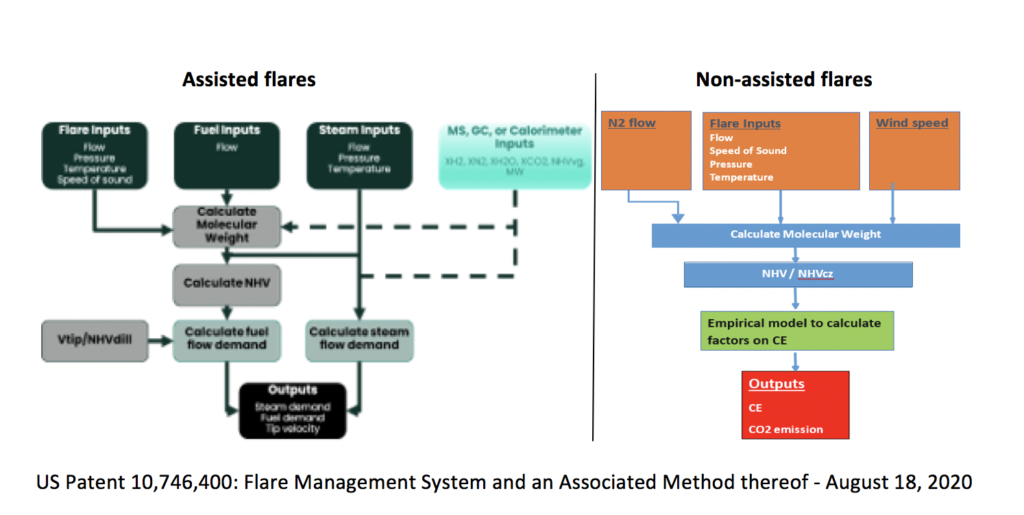
Advantages
The CE range is 50%-99.8% with an absolute error of 1.05% for CE% ≥ 95%
Easy to implement and set up, easy to tune to wide variety of flares
Flow meter vendor agnostic
Can work locally and/or be cloud based for unmanned assets
When there is a single flare boom with a single flame, it distinguishes LP flare from HP flare
Works with onshore and offshore facilities
Field proven with installations Downstream (33), Midstream LNG (4), Upstream (2) since 2017
Provides data on multiple flare parameters, such as flow rate, temperature, pressure, MW
Underlying measured parameters each have an estimate of uncertainty
Limitations
Requires an ultrasonic flowmeter on the flare line to feed data to the system
Inferred measurement (but verified with available online analyzers in Downstream facilities)
Validation relative to reference methods, such as extractive samplingThe process of measuring flaring combustion by extracting part of the plume and analysing the absolute quantities of burnt and unburnt gas by measn of a traceable method such as... Learn more..., is complex
Not fully deployed for methane management
Case study
Awaiting entry
The inclusion of feedback systems into flare monitoring allows adjustments to be made to how the flare is operated to maintain good combustion efficiency. As many influences on flares are transient - such as corsswinds, these systems need to operate in near real-time to afford the maximum benefits to the operation.