
Feature image courtesy of Zeeco, Inc.® – all rights reserved.
A spectrometer that provides direct and real-time measurement of flare combustion efficiency by measuring the ratio of methane to carbon dioxide. Energy radiated by the flare is used to measure CO2 and CH4 intensity in the combustion zoneThe area of the flare flame where the gas and vapours found just after a flare tip combine for combustion. Elevated Flare definitions and calculation methods from 40 CFR 63… Learn more…. It has been tested against established reference methods including extractive samplingThe process of measuring flaring combustion by extracting part of the plume and analysing the absolute quantities of burnt and unburnt gas by measn of a traceable method such as… Learn more…. VISR works for flares of all sizes and locations provided the flame can be isolated within the field of view
It can be deployed as a survey method or used as a permanently installed system (see separate entry).

Advantages
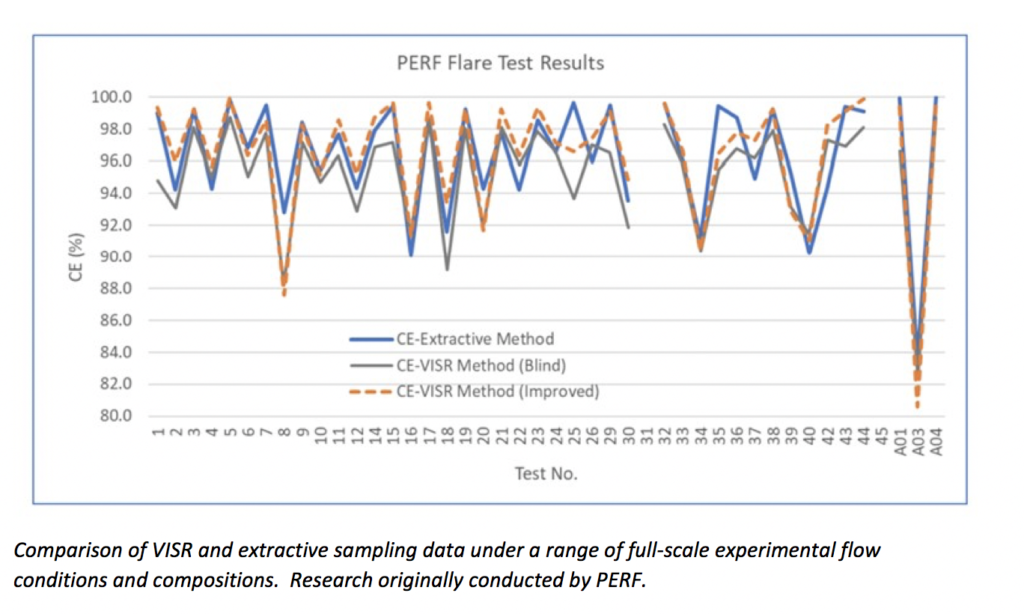
Results have been compared to the reference extractive method (see separate entry) with a mean difference - 0.07% in the 95-100% CE range
Tested against flares of variable size, design and with/without assist features
Quick (~30mins) setup, can be mobilised to provide measurements both onshore & offshore
Can be run from outside process boundary, camera being positioned 100-1000ft from flare
Directly measuring CE eliminates the uncertainty of using surrogate parameters (e.g. NHVcz)
Operates in a range of environmental conditions, day & night
Provides data on other flare parameters, including temperature, smoke index and flow rates
Limitations
Needs a clear line of sight of the full combustion envelope
Cannot measure the concentration of CO, hence, DE has to be empirically derived
Some limitations in severe weather conditions (e.g. heavy fog)
Case study
VISR was deployed for testing of flare destruction efficiency alongside four other performance indicators in an onshore conventional gas production site. Three flares were tested, two in the central processing facility and one well pad flare. Tests were performed at ~1000ft distance to flare, conducted over two days with each flare measurement lasting approx. 1 hour. Tests done during daytime with calm wind.
Example data
| Flare type |
Indicative flowrate (MMSCFD) |
VISR Destruction efficiency (DE) (%) |
DE Standard Deviation (%) |
|
LP |
0.65 |
99.0 | 0.5 |
|
HP |
1.6 | 97.0 |
0.8 |
|
Well pad |
3.6 | 98.2 |
2.1 |
Spectrometry is the observation and measurement of wavelengths of light or other electromagnetic radiation. Once a range of wavelengths, or a spectrum, for a gas mixture has been measured, by observing the intensity or amplitude of individual wavelengths, the method allows for determination of chemical composition of that gas mixture. Spectrometry is typically performed with the use of a spectrometer which is an instrument that separates and measures the spectral components of the sample or object being studied. Various types exist, but the most used are either a mass spectrometer or an optical spectrometer. Spectrometry techniques may be used for process control - such as determining the composition of flared gas, or for environmental measurements such as determination of combustion efficiency.