
A permanent IR system provides automatic monitoring of the flare system to ensure a reliable operation at all times. It is an optical system based on a real-time measurement of the wavelength of a distance source. Permanent IR can be applied to various flare types and sizes. Typically it is used to ensure functionality of the flare or pilot from a safe distance and is not a direct measurement of methane emissions, but changes in the flare performance may be indicative of changes to the efficiency.
Advantages
No direct access/physical contact to source required
Reliable 24/7 operation for monitoring gas flares by proven technology
Distances up to ¼ mile (400 meters) or even more possible
Applicable for various flare types: ground flares, elevated flares, offshore, staged
Immediate detection of extinguished pilot or permanent flames with direct alarming for quickest possible flame restart or stop of the gas flow
Installation in safe distance of the flare
Operates in range of conditions, day & night
Easy access for maintenance
Easy to install and upgrade existing facilities, scalable
Installation of a pan-tilt system can allow for monitoring of more than one flare at a time
Limitations
Not a direct measurement of methane emissions
Needs a clear line of sight
Does not provide any detailed information about the quality of combustion but rather only the operational status (on/off)
Some limitations in severe weather conditions (e.g. heavy fog/heavy rain)
Case study
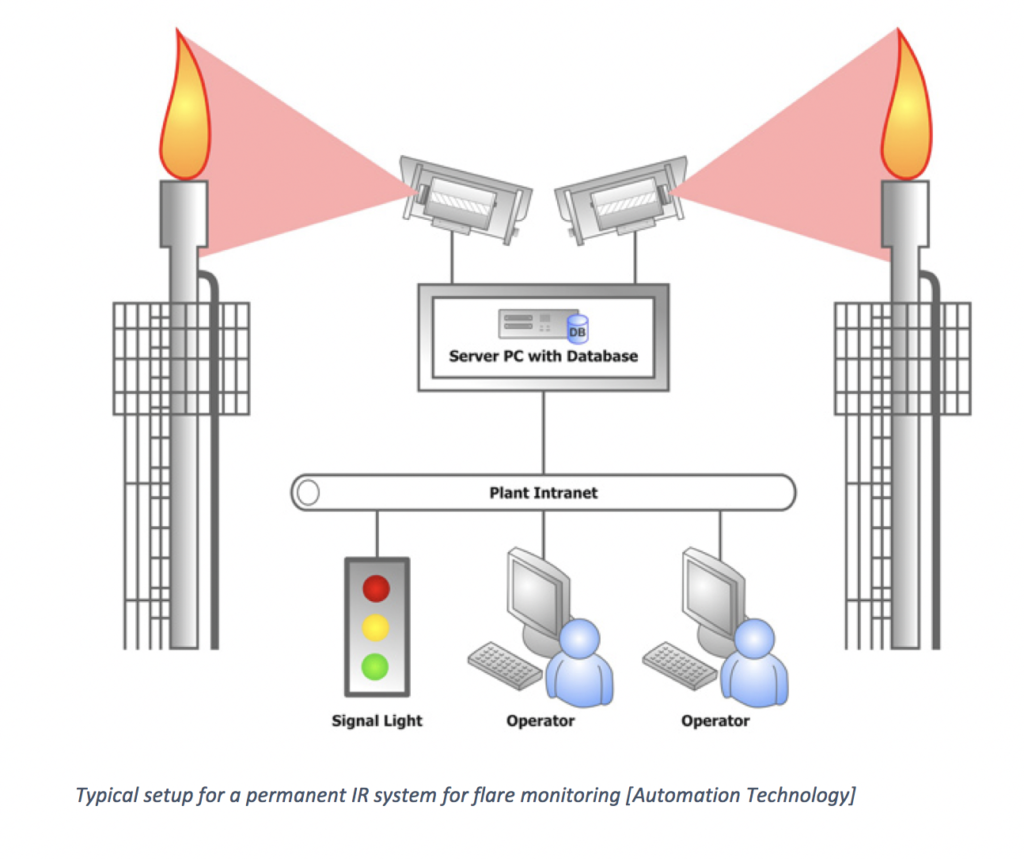
In a facility with two flare stacks a permanent IR system is installed. The pilot of each flare is monitored by an individual IR camera which is mounted in a safe distance to the flare as illustrated in the figure below. Its location close to the ground provides easy access for maintenance operation. The signals from the cameras are linked to a server with database and a web server. Information is then transferred to the plant intranet which feeds a signal light to show the operational status. The information is also accessible from the operations room. This setup ensure the continuous operation of the pilot and enables the operator to react quickly on any problems encountered.
Image courtesy of Automation Technology
Spectrometry is the observation and measurement of wavelengths of light or other electromagnetic radiation. Once a range of wavelengths, or a spectrum, for a gas mixture has been measured, by observing the intensity or amplitude of individual wavelengths, the method allows for determination of chemical composition of that gas mixture. Spectrometry is typically performed with the use of a spectrometer which is an instrument that separates and measures the spectral components of the sample or object being studied. Various types exist, but the most used are either a mass spectrometer or an optical spectrometer. Spectrometry techniques may be used for process control - such as determining the composition of flared gas, or for environmental measurements such as determination of combustion efficiency.